Notification infrastructure platforms may handle the complexity, but understanding each channel's unique challenges and capabilities will help you make more informed implementation decisions. Each channel has its own technical requirements, user expectations, and failure modes that require some understanding to really make them effective.
Push notifications
Push notifications are messages that appear on a user's mobile device or tablet even when they're not actively using your app. They're one of the most immediate and visible notification channels, which makes them both powerful but also disruptive to the user if not used judiciously.
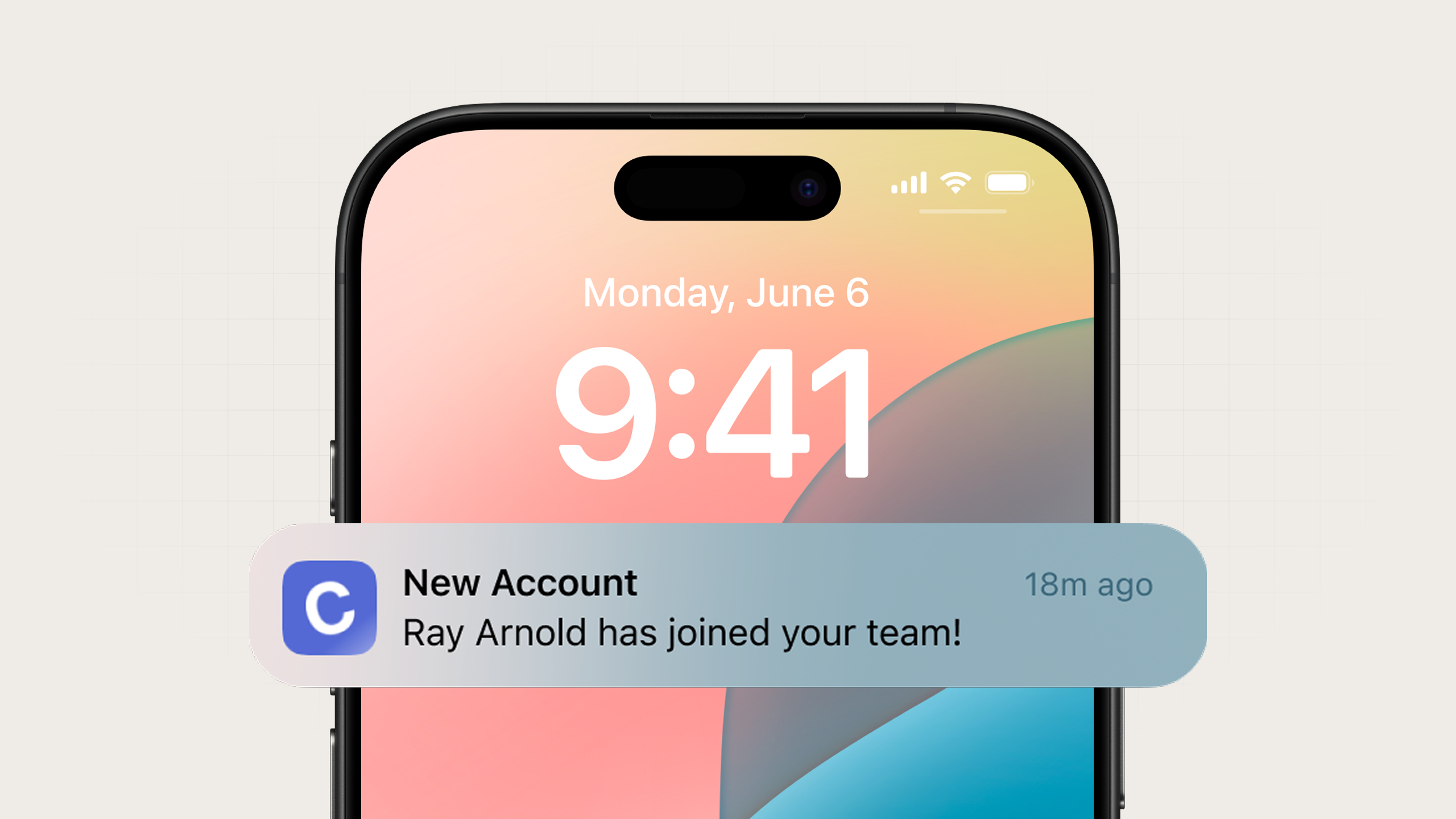
An example push notification
When to use push notifications
Push notifications are great for:
- Time-sensitive alerts like payment failures and security warnings.
- Real-time updates like breaking news or live event updates.
- Critical workflows like 2FA confirmations and appointment reminders.
- Re-engagement campaigns for dormant users.
But push notifications interrupt users. If you send too many or fail to make them relevant enough, users will disable them or, even worse, uninstall your app. We see many users opt in initially, but the rate drops quickly due to notification abuse.
Still, when used wisely, push can be a very effective channel to engage and retain users. Duolingo relies heavily on push notifications to keep users coming back to the app, and leverages an AI algorithm to manage conditional eligibility and messaging templates, ensuring messages are timely, personalized, and fresh.
The complexity of building push notifications
Building push notifications requires you to create a lot of system components to deal specifically with mobile devices and push providers. We wrote a comprehensive developer manual about implementing a push notification service if you want more detail. Below are just a few of the complexities involved with building your own service.
Manage platform differences
iOS requires APNs while Android uses FCM. Each has unique payload formats, size limits (typically 4 KB), and capabilities. Web push adds browser-specific endpoints with service worker requirements.
Handle token lifecycle
Device tokens fail silently. iOS tokens expire on reinstall, Android tokens rotate periodically, and web tokens die when users clear browser data. You need infrastructure to track freshness, process updates, and detect dead tokens—sending to invalid tokens wastes resources and triggers rate limits.
Implement reliable delivery
Push isn't guaranteed. Devices go offline, tokens expire, and services fail. You need exponential backoff for retries, dead letter queues, and fallback channels for critical messages.
Navigate rate limits
Apple and Google enforce undocumented limits to prevent spam. Send too fast and you're throttled. Most developers implement 3-5 pushes per hour per user, except for critical alerts.
How notification infrastructure simplifies push notifications
Notification infrastructure platforms handle the complexity of push notifications in several ways:
- Unified API: Instead of separate APNs and FCM integrations, one API handles routing and payload formatting. Channel groups enable one template to work automatically across iOS and Android.
- Automatic token management: When providers report invalid tokens, platforms remove them immediately. No manual cleanup, no wasted sends.
- Built-in reliability: Battle-tested retry logic, circuit breakers for failures, and automatic channel fallback. If push fails due to uninstall, route to SMS or email based on your workflow.
- Platform features preserved: Access iOS badge counts, Android notification channels, and deep linking through simple template overrides. Complete control when needed, simplicity by default.
Send push notifications with Knock
Knock eliminates push complexity through channel groups—one workflow step for both iOS and Android. Automatic token management removes invalid tokens immediately, and platform-specific features like badges, sounds, and deep links remain accessible through template overrides. Integration with Expo provides additional flexibility when needed.
In-app notifications
In-app notifications appear while users are actively using your application. Unlike push notifications that interrupt, in-app notifications enhance the active experience with real-time, contextual messages that the user can access on their own timeline.
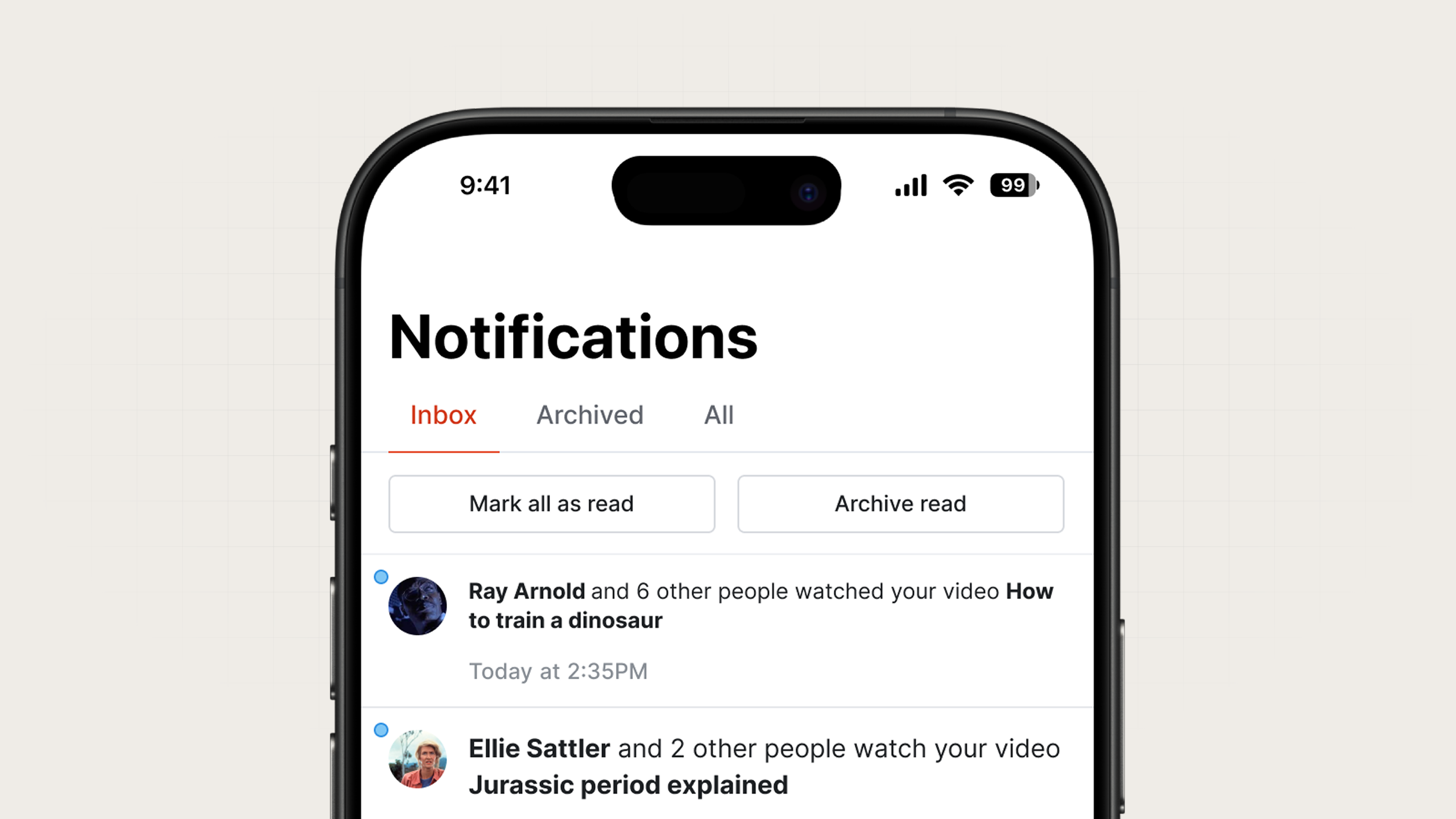
An example in-app notification feed
When to use in-app notifications
In-app notifications are great for:
- Social interactions like comments and mentions.
- Live collaboration updates like "John is editing."
- Real-time updates like "Payment processed."
- Progressive disclosure like onboarding tips and feature announcements.
The key advantage: consent. Users chose to use your app right now. This allows for frequent updates that would be annoying via push, such as every message in an active chat. Rich interactions (forms, videos, workflows) work naturally since users are already engaged.
The complexity of building in-app notifications
Building in-app notifications requires solving distributed systems problems. Below are just a few of the complexities involved with figuring this out.
Real-time connections
WebSockets provide instant delivery but need connection management, reconnection logic, and heartbeat monitoring. Scaling WebSocket servers requires sticky sessions or complex message routing. Not all networks support WebSockets, so you need HTTP fallbacks.
Cross-device state sync
Users have multiple tabs and devices open. Read a notification on your phone—it must instantly mark as read on your laptop. This requires distributed state management, conflict resolution, and careful ordering. "Sarah liked your post," followed by "Sarah unliked your post" must arrive in sequence.
State lifecycle tracking
Each notification has multiple states (delivered, seen, read, archived) that must persist and sync. Handle offline users who expect to see missed notifications. Manage the sacred notification bell—that badge count must be accurate across all devices.
Smart batching
Prevent notification spam through time-based batching ("5 new messages"), type-based grouping ("Sarah and 12 others liked your post"), and priority queuing. Balance responsiveness with overwhelming users. Paginate feeds efficiently—loading thousands of old notifications crushes performance.
How notification infrastructure simplifies in-app notifications
Notification infrastructure platforms handle the complexity of in-app notifications in several ways:
- Managed real-time infrastructure: Platforms provide WebSocket connections with automatic reconnection, message ordering, and fallback strategies. No sticky sessions or scaling concerns.
- Automatic state synchronization: Built-in states (unseen, seen, read, archived) sync across devices instantly. Read on phone, updates on laptop. Offline persistence ensures users never miss notifications.
- Intelligent batching: Configurable batching by time windows or event counts. Priority queuing for critical alerts. Automatic pagination and archival for performance.
- Flexible integration: Pre-built components for React or APIs for custom implementations. Feed filtering, custom styling, and engagement tracking included.
Send in-app notifications with Knock
Knock provides pre-built, in-app messaging components like feeds, banners, and pop-ups through pre-built React components or flexible APIs. Managed WebSocket connections handle real-time delivery without building sync logic, and the feed API provides pagination, filtering, and batching. Headless components give engineering teams complete UI control, with engagement tracking included.
Email notifications
Email remains the workhorse of notification channels. It's universal, persistent, and rich, but also complex. What seems like a simple SMTP send quickly becomes a battle with spam filters, reputation management, and inbox placement.
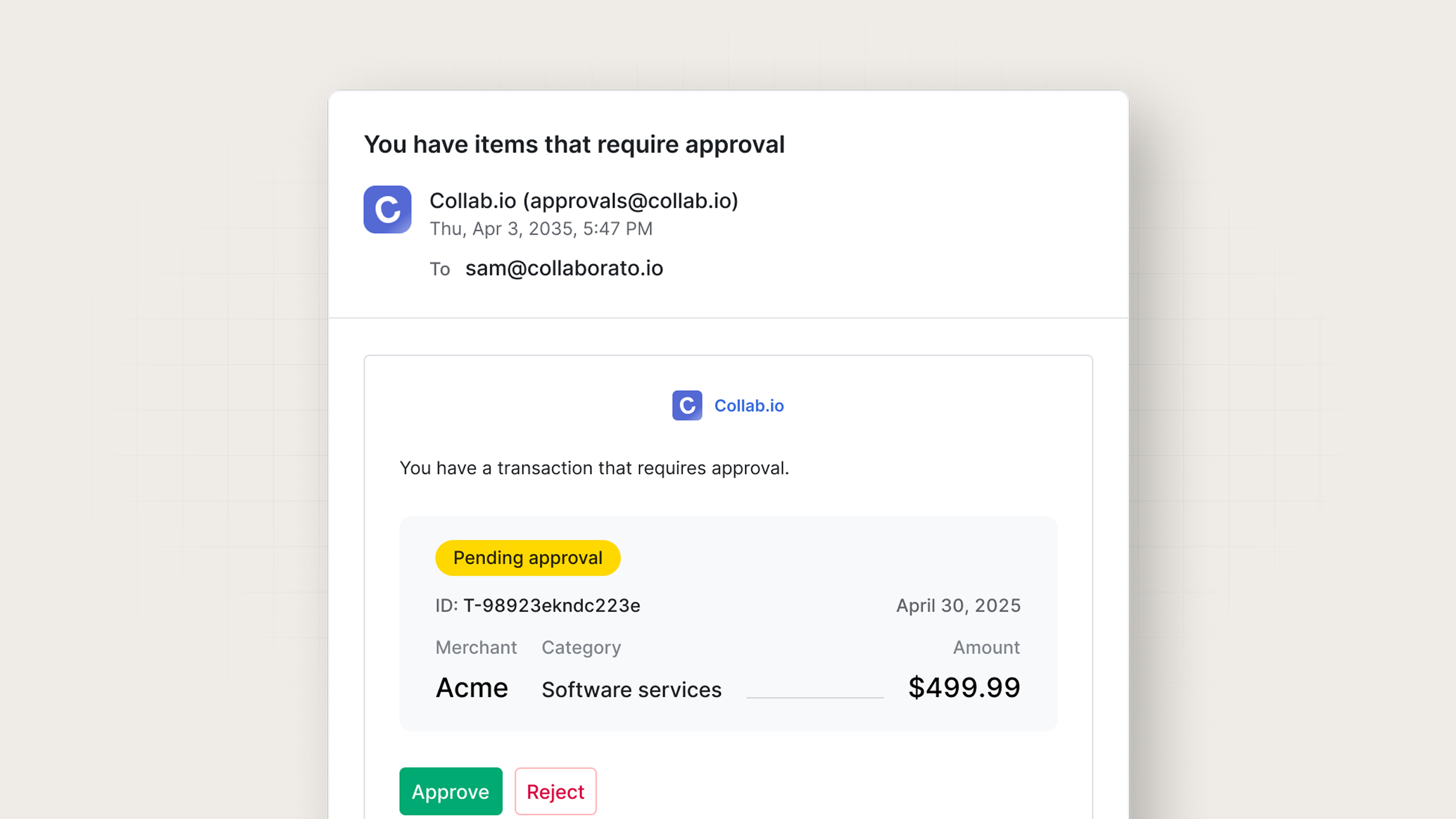
An example email notification
When to use email notifications
Email excels for transactional records (receipts, invoices), digest notifications (daily summaries, reports), long-form content (newsletters, onboarding materials), and legal requirements (term updates, audit trails).
Email is universal—everyone has it, expects it, and knows how to search it. However, open rates only average around 45% for transactional emails, delivery isn't instant, and spam folder placement can significantly impact engagement.
The complexity of building email notifications
We wrote a comprehensive developer manual about implementing a transactional email service if you want more detail. Below are just a few of the complexities involved with building your own service.
Deliverability warfare
Modern providers (Gmail, Outlook) use sophisticated spam detection, examining your IP reputation, domain authentication (SPF/DKIM/DMARC), content patterns, and engagement rates. Your sender reputation acts like a credit score—every bounce, spam complaint, or low engagement damages it across all providers.
Rate limit orchestration
ESPs enforce complex limits, including hourly caps, burst rates, and domain-specific throttling. Gmail might accept 2000 emails per day, while Yahoo allows 500 emails per hour. Intelligent queuing must prioritize password resets over newsletters while respecting these limits.
Template management sprawl
Multi-language support, personalization, A/B testing, and brand consistency create template chaos. HTML emails must work across dozens of clients with different rendering quirks. Design changes require deployments, so marketing teams get stuck without engineering resources.
Persistence responsibility
Unlike ephemeral push notifications, emails last forever. They get forwarded, archived, and subpoenaed. This permanence requires careful content design and legal compliance (CAN-SPAM, GDPR).
How notification infrastructure simplifies email notifications
Notification infrastructure platforms handle the complexity of email in several ways:
- Managed deliverability: Platforms handle authentication setup, IP warming, reputation monitoring, and bounce processing. They maintain relationships with ISPs and adapt to changing requirements.
- Visual template systems: Drag-and-drop editors with version control. Automatic plain-text generation. Multi-language support with locale detection. Preview across email clients without manual testing.
- Intelligent sending: Automatic rate limit management across providers. Priority queues for critical emails. Time zone awareness for optimal delivery. Batch collection for digest emails.
- Compliance built-in: Automatic unsubscribe handling, preference centers, and audit logs. Provider switching without workflow changes.
Send email notifications with Knock
Knock automates email complexity through managed, provider-agnostic templates that work seamlessly with SendGrid, SES, Postmark, and other providers. Link tracking, custom headers, and per-environment configuration are included, and batch sending can collect multiple triggers into digests automatically to reduce notification fatigue. The visual editor supports markdown with Liquid personalization, shared partials, automatic translations, and instant rollback.
SMS notifications
SMS delivers text messages directly to mobile phones via cellular networks. It's the most reliable notification channel (no internet required, no app to install, near-universal reach), but also the most constrained and expensive.
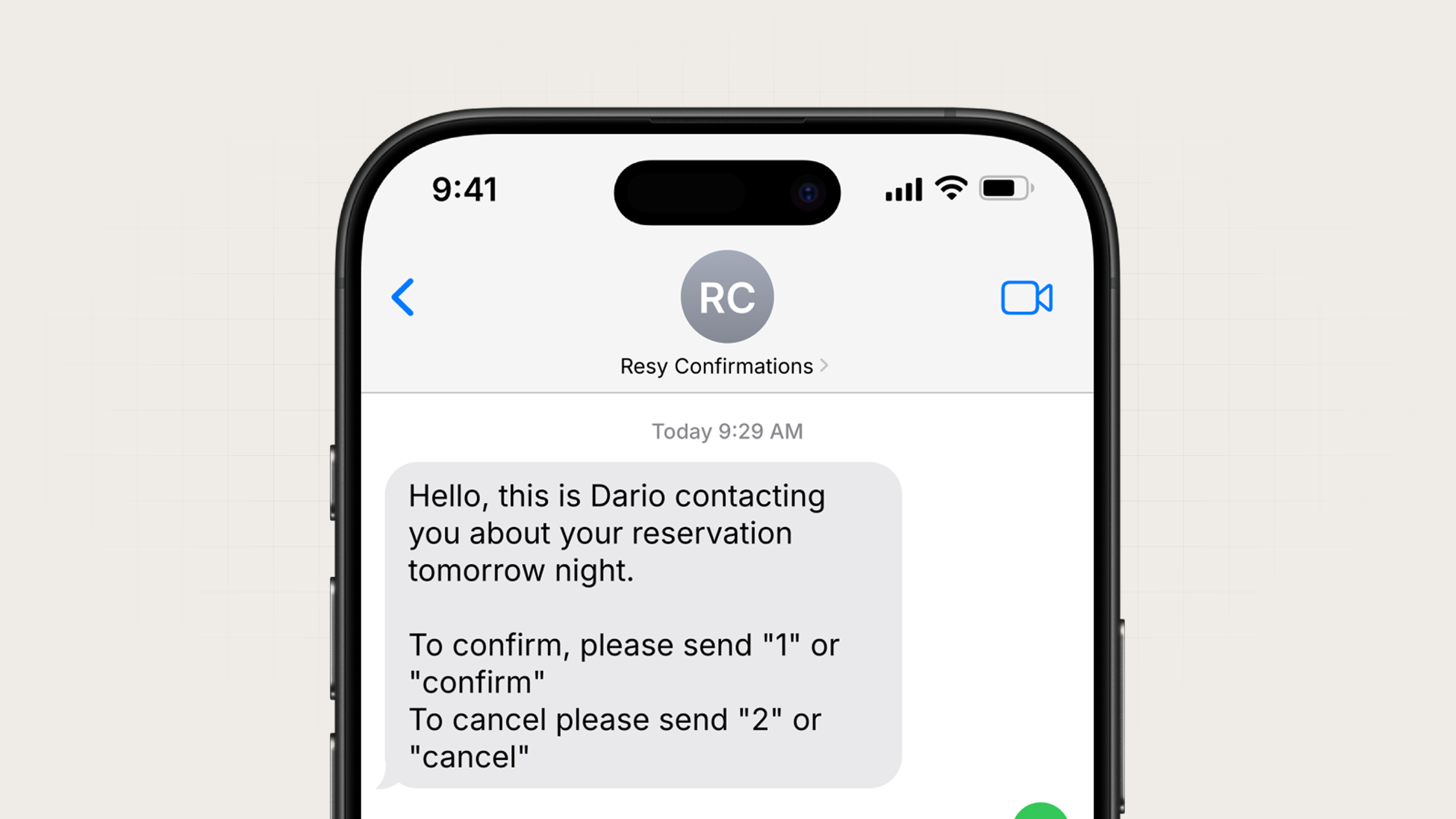
An example SMS notification
When to use SMS notifications
SMS excels for authentication notifications, critical alerts like fraud warnings and outages, time-sensitive reminders like appointments and deliveries, and as a fallback when other channels fail.
While 90% of SMS messages are read within 3 minutes, phone numbers rarely change, and SMS works globally without apps or internet, SMS should be reserved for messages that justify interrupting users, due to their intrusive nature and high send cost.
The complexity of building SMS notifications
The simplicity of SMS is quickly masked by significant technical and regulatory challenges. Below are just a few of the complexities involved with sending effective, legal SMS messages.
Character limit mathematics
SMS uses 160-character segments, but special characters (emojis, accents) reduce this to 70. A 161-character message costs double. Every variable must be calculated: a long {{name}} could push you over the limit and double your costs.
Cost management at scale
SMS costs 100-1000x more than other channels. US messages cost $0.01-0.02, but international messages can exceed $0.30. Without careful controls, a notification bug can generate thousands in unexpected charges.
International complexity
Every country has different rules. Some require pre-registered sender IDs, others only accept phone numbers. Content filters block URLs or keywords. Delivery rates vary from 95% (US) to 70% (some international routes). E.164 formatting is mandatory but often mishandled.
Regulatory minefield
The US requires 10DLC registration with business verification. TCPA penalties reach $1,500 per unauthorized message. GDPR applies in Europe. Opt-in requirements, STOP handling, time restrictions, and audit trails are legally mandated.
How notification infrastructure simplifies SMS notifications
Notification infrastructure platforms handle the complexity of SMS notifications in several ways:
- Intelligent truncation: Platforms count characters in real-time during template design, warning about segment breaks. Smart variable handling prevents words from being split across segments.
- Cost controls: Set budgets with automatic fallback to email when exceeded. Route by region to the most affordable and reliable providers. Monitor spend anomalies.
- Global delivery: Platforms maintain provider relationships worldwide, handle country-specific requirements, and format numbers correctly. They navigate sender ID registration and content restrictions.
- Compliance automation: Automatic STOP handling, opt-out lists, delivery windows, and audit logs. Platforms track consent and handle regulatory requirements across jurisdictions.
Send SMS notifications with Knock
Knock abstracts SMS complexity through provider-agnostic architecture (Twilio, Vonage, AWS SNS, others) that includes the ability to switch providers without changing workflows—Knock normalizes API differences and requirements. Automatic compliance features include STOP handling, opt-out management, and delivery windows, while link tracking works through automatic URL shortening with custom domains.
Chat notifications
Chat-based notifications deliver messages directly into communication tools where teams spend their working hours. Unlike email that sits unread, or push notifications that get disabled, chat notifications typically land in active conversation streams.
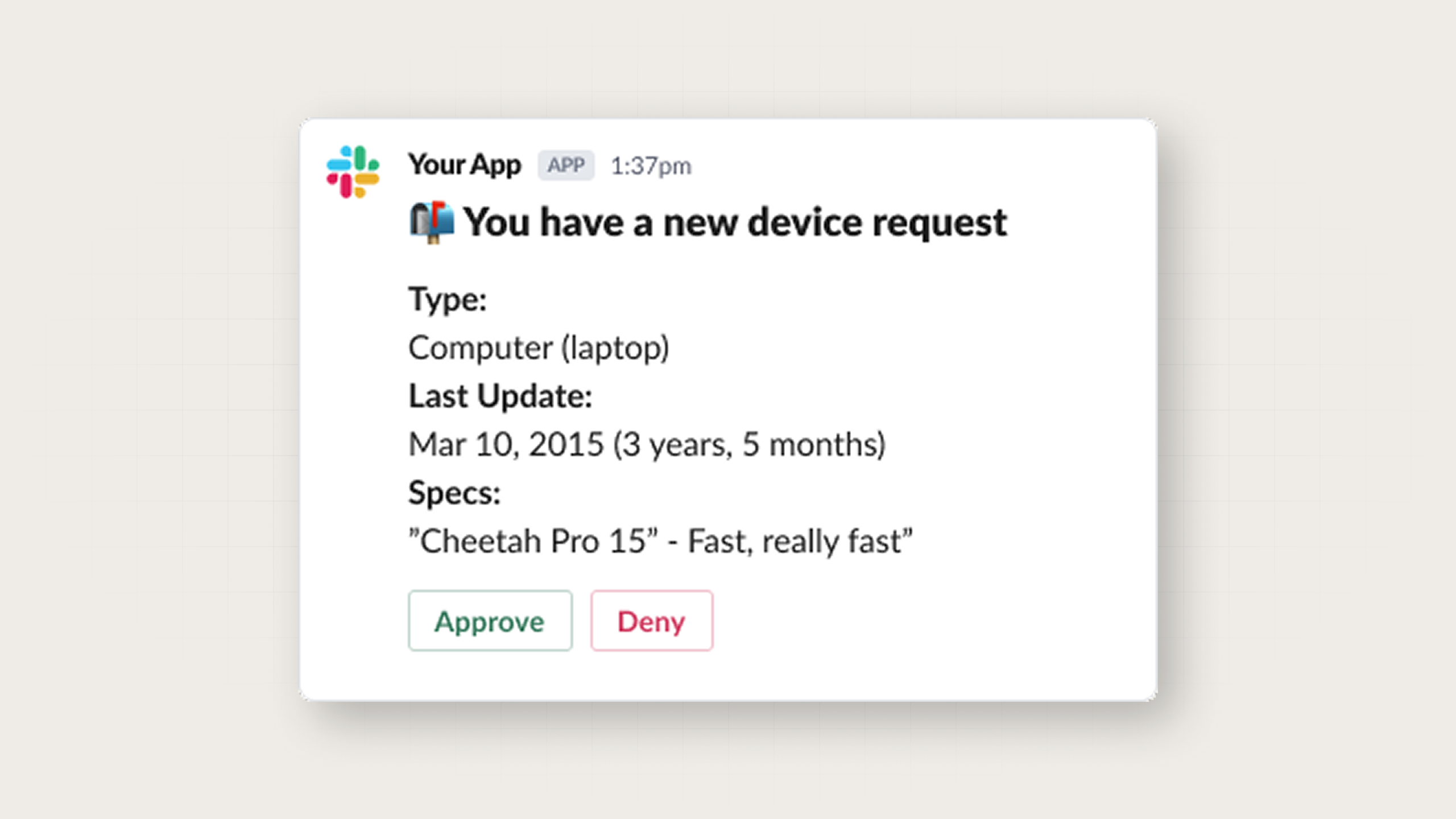
An example Slack notification
When to use chat notifications
Chat notifications are a more niche channel, typically only relevant for messaging users at work. For example, a B2B SaaS product like Ramp will have the best case for needing to update their users in Slack, while Slack or Teams would not be a good channel for a consumer app like Netflix.
Even the most common chat apps carry different user expectations and justify different approaches:
- Slack: Essential for B2B SaaS—direct messages for personal alerts, channel messages for team updates, interactive notifications for approvals and workflows.
- Teams: Enterprise environments with Office 365 integration—adaptive cards for complex workflows.
- Discord: Communities, education, and remote teams—rich embeds with persistent, searchable history.
- WhatsApp: Global reach with 2B+ users—transactional messages, appointments, and support in regions where it's primary communication.
The complexity of building chat notifications
Each chat platform presents unique integration challenges. Below are just a few of the complexities involved with sending highly customizable messages in various chat platforms.
Platform fragmentation
Slack uses Block Kit JSON, Discord uses markdown with custom extensions, Teams uses Adaptive Cards, and WhatsApp requires pre-approved templates. Every platform has different rate limits—Slack allows one posted message per second per channel, Discord allows 50 messages per second, and Teams allows 50 requests per second. Building abstractions for these differences is complex.
Bot infrastructure at scale
Chat notifications require bot applications that handle authentication, token rotation, and event processing. A successful Slack app might be installed in thousands of workspaces, each generating events. You need webhook signature verification, idempotent processing, and graceful error handling.
Message formatting maze
Bold text, mentions, and links have different syntax per platform. Interactive elements (buttons, forms) have completely different implementations. URLs behave differently—Slack auto-unfurls, Discord shows embeds, and Teams generates previews.
Enterprise requirements
Slack requires OAuth for each workspace installation. Teams needs IT approval and tenant permissions. WhatsApp mandates template pre-approval with lead times. Each platform has different security, compliance, and data residency requirements.
How notification infrastructure simplifies chat notifications
Notification infrastructure platforms handle the complexity of chat notifications in several ways:
- Unified templating: Write in markdown once, and platforms translate to Block Kit, Adaptive Cards, or Discord embeds automatically. Platform-specific features are accessible through consistent syntax.
- Managed connections: Platforms handle OAuth flows, token storage, and rotation. Automatic workspace installation for Slack and Microsoft Teams. Template approval management for WhatsApp.
- Smart rate limiting: Automatic queuing respects each platform's limits. Messages delivered at maximum safe speed without triggering 429 errors.
- Cross-platform features: Link tracking, delivery status, and error handling work consistently across all chat platforms. Channel groups enable fallbacks—try Slack first, fall back to email if not connected.
Send chat notifications with Knock
Knock simplifies chat complexity through unified markdown templating, which translates to each platform's native format. JSON templates provide full platform capabilities when needed. Channel groups enable intelligent routing—one workflow attempts multiple chat platforms with automatic fallback. Ideal for B2B products with diverse customer needs and preferences.
Connection management varies by platform, but Knock handles the complexity of OAuth for Slack and Teams, webhooks for Discord, and API credentials for WhatsApp. Automatic rate limiting, token management, and cross-platform link tracking included.